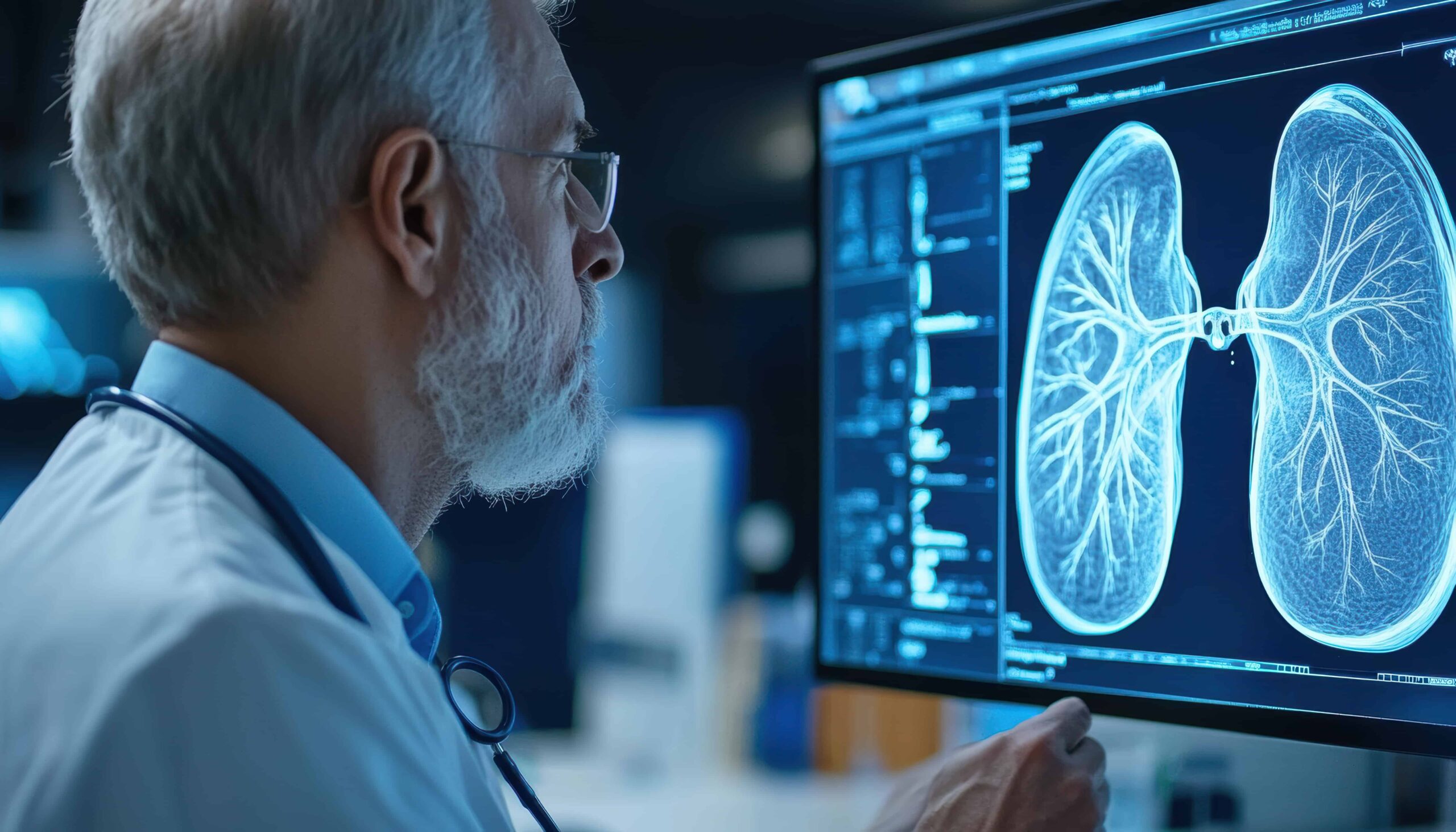
Breathing is something most people take for granted, until it becomes difficult. The average person breathes nearly 25,000 times per day, but for people living with lung conditions, each breath can be a challenge. That’s why PACT is committed to treating people with lung conditions in Connecticut, whether they’re living with COPD, asthma, pneumonia, or another lung condition.
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
COPD is a progressive lung disease that affects 5.3% of adults in Connecticut. It’s caused by damage to the lungs, which can lead to inflammation and other problems.
Symptoms
The symptoms of COPD tend to develop slowly, and in the early stages, may be mistaken for aging or poor fitness. As the disease progresses, the symptoms get worse and can affect your daily activities. Some symptoms of COPD include:
- Chronic cough
- Coughing up mucus
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty taking a deep breath
- Chest tightness
- Wheezing
Risk Factors
Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of COPD. However, even people who’ve never smoked can develop the disease. Long-term exposure to other lung irritants, such as air pollution, smoke from wood stoves, or workplace chemicals, may increase the risk of developing COPD. Other risk factors include having asthma or being over 40.
Treatment Options
Many treatment options may help control your symptoms and slow the progression of COPD. Your pulmonologist may recommend medications to make breathing easier, supplemental oxygen to help you get the air you need, or pulmonary rehabilitation to teach breathing techniques.
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic lung condition that causes your airways to narrow and swell, making it harder to breathe. In Connecticut, 10.8% of adults report being diagnosed with asthma.
Symptoms and Common Triggers
Asthma symptoms are also known as a flare-up or an attack. They can be triggered by a wide range of things, including poor air quality, respiratory infections, exercise, stress, or allergens like mold and pollen.
When asthma symptoms occur, they can range from mild to severe. You may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Wheezing
- Chest pain or tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
- Waking up at night due to breathing difficulties
Pediatric vs. Adult Asthma
Childhood asthma and adult asthma have similar symptoms, but differ in how they’re managed. In children, asthma symptoms often come and go and may go into remission as they get older. In adults, asthma symptoms tend to be more severe and are less likely to improve over time.
Preventing and Managing Asthma Attacks
Asthma is typically treated with two types of prescription medications: long-term control medicines to reduce airway inflammation and prevent attacks, and quick-relief inhalers to open airways during an attack. Doctors may also recommend specific lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and limiting known triggers.
Bronchitis & Pneumonia
Bronchitis and pneumonia are lower respiratory infections that make it harder to breathe. Bronchitis affects the airways leading to your lungs, while pneumonia affects the air sacs in the lungs.
Bronchitis or Pneumonia? How to Tell the Difference
Since bronchitis and pneumonia cause similar symptoms, it’s not always easy to tell them apart. Bronchitis can be acute (lasting 10-14 days) or chronic (lasting more than three months), and typically causes symptoms such as: A cough that produces yellow or green mucus.
- Stuffy or runny nose
- Mild fever
- Body aches or headaches
Pneumonia causes many of the same symptoms as bronchitis, along with more severe symptoms such as:
- High fever
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Chills and sweating
Managing Bronchitis and Pneumonia
Acute bronchitis usually gets better on its own, though sometimes, antibiotics are needed to clear up the infection. Chronic bronchitis is typically managed with medications or therapies to help you breathe better.
Pneumonia may require more intensive treatment to prevent complications, especially for people in high-risk groups like infants or seniors. Treatment may include antibiotics or other medications, or in some cases, hospital care.
When to Seek Urgent Care
Pneumonia can be a life-threatening condition, so it’s essential to seek prompt care. See your doctor right away if you experience severe symptoms, such as:
- A long-lasting cough
- Coughing up pus
- Chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- A lingering fever of 102°F or higher
Lung Cancer Screening & Management
Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers in both men and women. In 2025, about 226,650 Americans are expected to be diagnosed with it, but with early detection, it’s more likely to be successfully treated.
Early Signs of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer symptoms can be easy to overlook because they’re similar to those of other, less serious illnesses. Some common signs of lung cancer to watch out for include:
- Persistent or worsening cough
- Coughing up blood
- Loss of appetite or unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Recurring bronchitis or pneumonia
Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines in CT
Lung cancer screening uses low-dose CT scans to detect cancer early. The US Preventive Services Task Force recommends annual screening for people aged 50 to 80 who smoke or quit within the last 15 years. In Connecticut, nearly one-quarter of high-risk people are screened, far higher than the national average.
PACT’s Referral and Care Process
At PACT Pulmonology, patients who are diagnosed with lung cancer are quickly referred to an oncologist for appropriate treatment. Your PACT pulmonologist may coordinate with the oncologist to manage respiratory issues that arise during treatment.
When to See a Pulmonologist in Connecticut
Pulmonologists are doctors who specialize in diagnosing and treating lung conditions. Your primary care doctor may refer you to a pulmonologist if you have chronic symptoms or breathing issues, such as a cough that doesn’t go away, asthma attacks, or repeated infections.
At PACT, your care is part of a larger system. If you need referrals to other specialists, such as cardiologists or surgeons, we coordinate the next steps for you and ensure your relevant records are shared with your care team for a smooth experience.
Breathe Easier with PACT
PACT Pulmonology is committed to providing comprehensive, patient-centered care to people living with a variety of lung conditions in Connecticut, including asthma and COPD. With locations in both Guilford and Orange, there’s a PACT Pulmonology office in your neighborhood. Schedule your respiratory evaluation today and get expert care tailored to your lung health needs.